Effects of heteroatom doping of carbon dots from sugar on optical properties, phenolic content, antioxidant activity, photostability, and cytotoxicity
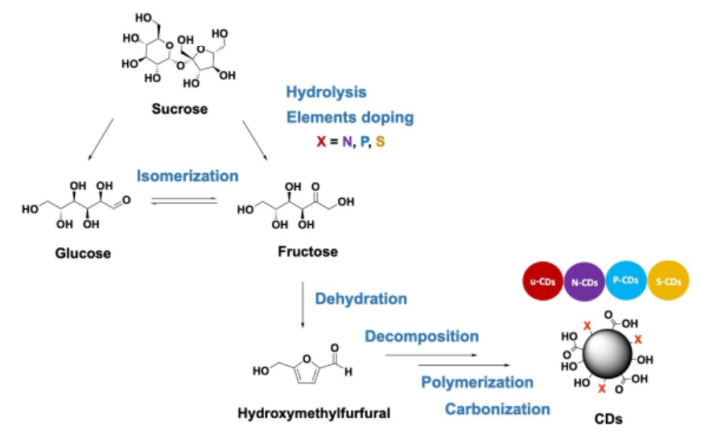
Our group recently collaborated with Dr. Peerasak Paoprasert from the Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Technology, Thammasat University in developing a method for the synthesis and heteroatom doping of carbon dots from sugar using nitric acid, phosphoric acid, and sulfuric acid as catalysts and dopants. Carbon dots (CDs) are nanomaterials used in several applications, such as sensors, bioimaging, cell tracking, and drug delivery. Our work demonstrated that the undoped CDs were the most biocompatible and had the highest UV-vis absorpition, phenolic content, antioxidant activity, and photostability, and these data will be important for selecting a proper choice of precursor for the development of high-performance, non-toxic applications.
Reference
Supjaroenpisan M, Hanchaina R, Kangsamaksin T, Paoprasert P. Effects of heteroatom doping of carbon dots from sugar on optical properties, phenolic content, antioxidant activity, photostability, and cytotoxicity. ChemistrySelect. 2021;6:3597–604. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202100495
| Relevant SDGs | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| BC investigator | |
 Assoc. Prof. Thaned Kangsamaksin Assoc. Prof. Thaned Kangsamaksin |
