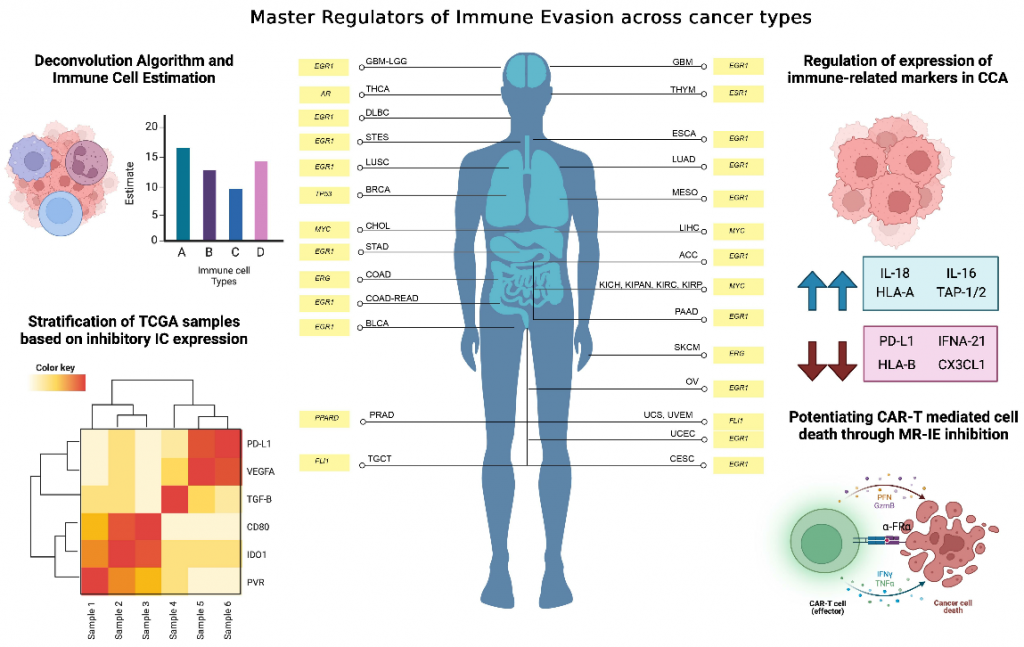
Current immunotherapies are ineffectively designed toward single-target inhibition in a complex multifactored process. Moreover, available therapeutics are incapable of meeting the needs of the expanding cancer patient population due to resistance, recurrence, immune-related adverse events, or patients that do not express the intended target. This study proposes Master Regulators of Immune Evasion (MR-IE) inhibition as a more effective systemic therapeutic strategy that targets multiple immune evasion molecules to reinstate immune recognition and the elimination of tumors. Moreover, this study also identifies and ranks ideal candidate MR-IEs for each cancer type associated with patient mortality. This study has been validated in cholangiocarcinoma. This investigation offers MR-IE as a new avenue of therapeutic targets that can be validated and developed as an immunotherapeutic strategy for all cancer types. Moreover, we address that not all cancers would respond to the same target, and thus, we propose mortality-associated MR-IEs per cancer type.
การรักษาด้วยวิธีการ “ภูมิคุ้มกันบำบัด” คือการกระตุ้นให้ภูมิคุ้มกันของร่างกายสามารถจัดการกับมะเร็งได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ และถือว่าเป็นการรักษาที่มีศักยภาพและมีประสิทธิภาพดีกว่าการรักษาด้วยวิธีการดั้งเดิม เช่น การใช้ยา รังสี หรือ การผ่าตัด แต่ที่ผ่านมาการรักษาด้วยวิธีนี้ยังไม่ได้ผลดีเท่าทีควร เหตุผลหนึ่งก็คือ การรักษาด้วยวิธีการ “ภูมิคุ้มกันบำบัด” มักจะมุ่งเป้ายับยั้งโมเลกุลเป้าหมายเพียงชนิดเดียว ในขณะที่มะเร็งเกิดจากความผิดปกติของหลายโมเลกุล ดังนั้น ในงานวิจัยชิ้นนี้ เราแสดงให้เห็นว่า เมื่อยับยั้งโมเลกุลเป้าหมายหลายๆโมเลกุลพร้อมๆกัน เซลล์ภูมิคุ้มกันจะทำลายเซลล์มะเร็งได้ดีขึ้น ในงานนี้ เราได้ใช้วิธีการทางชีวสารสนเทศ (bioinformatics) และพบว่า Myc เป็นโมเลกุลที่เป็นตัวควบคุมระบบภูมิคุ้มกัน (Master Regulator of Immune Evasion, MR-IE) ในมะเร็งท่อน้ำดี (Cholangiocarcinoma, CCA) เปรียบเสมือน Myc เป็น master switch/master regulator เราตั้งสมมุติฐานว่า ถ้ายับยั้ง Myc น่าจะทำให้หลายๆยีนที่อยู่ภายใต้การควบคุมของ Myc ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับกระบวนการ immune evasion ถูกยับยั้งไปด้วย ซึ่งน่าจะส่งผลให้กระบวนการ immune evasion ของมะเร็งอ่อนแอลงอย่างมากและทำให้เซลล์ภูมิคุ้มกันทำลายเซลล์มะเร็งท่อน้ำดีได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ เราได้ validate สมมุติฐานนี้โดยใช้ CAR-T cells และ CCA cell lines ในห้องปฏิบัติการและพบว่าผลเป็นไปตามสมมุติฐาน ดังนั้น การยับยั้ง Myc จึงเป็นทางเลือกที่น่าสนใจในการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการรักษาด้วย “ภูมิคุ้มกันบำบัด” ในมะเร็งท่อน้ำดี นอกจากนี้ งานวิจัยนี้ได้แสดงว่าโมเลกุลที่ทำหน้าที่ MR-IE ในมะเร็งแต่ละชนิดมีความแตกต่างกัน ดังนั้นจึงเป็นสิ่งที่น่าศึกษาต่อไปว่า การยับยั้ง MR-IE ในมะเร็งชนิดต่างๆเหล่านั้น จะช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการรักษาด้วย “ภูมิคุ้มกันบำบัด” เช่นเดียวกับมะเร็งท่อน้ำดีดังที่แสดงในงานวิจัยนี้หรือไม่
Reference
Venkatraman S, Balasubramanian B, Kongpracha P, Yangngam S, Chuangchot N, Khanaruksombat S, Thongchot S, Suntiparpluacha M, Myint KZ, Soodvilai S, Janvilisri T, Jirawatnotai S, Thuwajit P, Thuwajit C, Meller J, Chutipongtanate S*, Tohtong R*. Identification of transcriptional regulators of immune evasion across cancers: An alternative immunotherapeutic strategy for cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers 2024;16(24):4197.
Relevant SDGs

BC investigator

