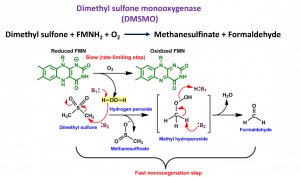
Dimethyl sulfone monooxygenase catalyzes the oxidative cleavage of dimethyl sulfone (DMSO2) to produce methanesulfinate and formaldehyde. It is a two-component monooxygenase composed of a reductase component (DMSR) and a monooxygenase (DMSMO). This study has used combined transient kinetics and product analysis using HPLC-MS to reveal the mechanism of C-S bond cleavage for the first time. The results of the analysis of H2O2 production demonstrated the use of H2O2 in oxidative C-S bond cleavage, by which the H2O2 produced from DMSMO and oxygen reactions can rapidly react with the DMSO2 substrate and initiate the C-S bond cleavage. Understanding the reaction mechanism from the rapid kinetic study serves as knowledge pertaining to future enzyme structural studies and enzyme engineering for biobased degradation of toxic volatile sulfur compounds in wastewater treatments.
Reference
Mangkalee M, Oonanant W, Aonbangkhen C, Pimviriyakul P, Tinikul R, Chaiyen P, Insin N, Sucharitakul J. Reaction mechanism and kinetics of the two-component flavoprotein dimethyl sulfone monooxygenase system: Using hydrogen peroxide for monooxygenation and substrate cleavage. FEBS J. 2023 Jul 31.
DOI: 10.1111/febs.16916.
| Relevant SDGs | |
|---|---|
| BC investigator | |
 Asst. Prof. Ruchanok Tinikul Asst. Prof. Ruchanok Tinikul |
|