English
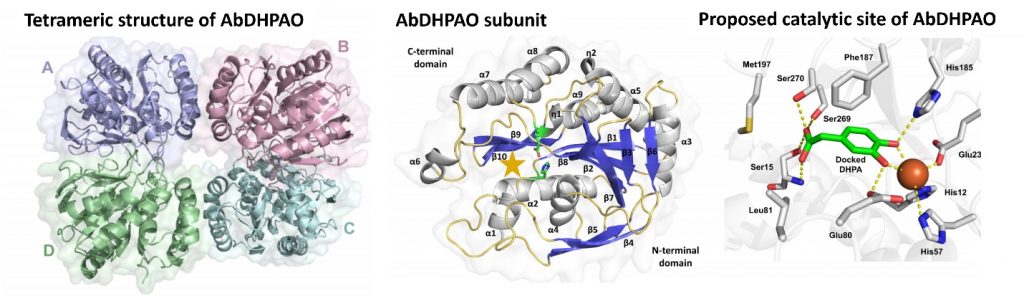
In this study, we report the structure and biochemical characterization of 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetate (DHPA) 2,3-dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.15) from Acinetobacter baumannii (AbDHPAO), which is a Fe2+ specific enzyme. This is an enzyme that catalyzes the 2,3-extradiol ring-cleavage of DHPA in the p-hydroxyphenylacetate (HPA) degradation pathway. The 1.8 Å X-ray structure of apo-AbDHPAO revealed four subunits per asymmetric unit, consistent with a homotetrameric structure. The AbDHPAO structure is αβ-sandwiched fold, which is different from the dual β-barrel-like motif of the well-characterized B. fuscum DHPAO structures. But the enzyme shares the same chemistry owing to a conserved 2-His-1-carboxylate catalytic motif. Structure analysis and molecular docking revealed substrate binding site consists of the conserved residues His12, His57, and Glu238 forming a 2-His-1-carboxylate motif ligating to Fe2+ cofactor. Substrate specificity also demonstrates the ability of AbDHPAO to accomudate 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate derivatives with different aliphatic carboxylic acid substituents as substrates. This report provides a better understanding of the structure and biochemical properties of AbDHPAO, which pave the way to future applications in linin utilization from biomass.
Thai
ในการศึกษานี้ได้รายงานการศึกษาโครงสร้างและลักษณะทางชีวเคมีของเอนไซม์ 3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl-acetate (DHPA) 2,3-dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.15) จากเชื้อ Acinetobacter baumannii (AbDHPAO) ที่เร่งปฏิกิริยาการแตกวงแหวนแบบ 2,3-extradiol ของ DHPA ที่พบในวิถีการย่อยสลาย p-hydroxy-phenylacetate (HPA) โดยโครงสร้างเอ็กซ์เรย์ในระดับความละเอียด 1.8 Å ของ apo-AbDHPAO เผยให้โครงสร้างโฮโมเตตระเมอร์ โดยโครงสร้าง AbDHPAO มีการม้วนพับแบบ αβ-sandwich ซึ่งแตกต่างจากลักษณะโครงสร้างที่เป็นการม้วนพับแบบ β-barrel ที่มีรายงานมาก่อนหน้านี้ของโครงสร้าง B. fuscum DHPAO อย่างไรก็ตามเอนไซม์ AbDHPAO นั้นมีคุณสมบัติทางเคมีในการเร่งปฏิกิริยาคล้ายกับเอนไซม์อื่นๆ ในกลุ่มนี้ ที่มี 2-His-1-carboxylate ในบริเวณเร่ง นอกจากนี้จากการวิเคราะห์โครงสร้างระดับโมเลกุลเผยให้เห็นตำแหน่งการจับซับสเตรตที่ประกอบด้วยเรซิดิวอนุรักษ์ His12, His57 และ Glu238 ที่สร้างโมทีฟ 2-His-1-carboxylate ที่ยึดเกาะกับโคแฟกเตอร์ Fe2+ การศึกษาความจำเพาะของสารตั้งต้นยังแสดงให้เห็นถึงความสามารถของ AbDHPAO ในการเร่งปฏิกิริยาของอนุพันธ์ของ DHPA ที่มีหมู่กอะลิฟาติกและคาร์บอกซิลิกที่แตกต่างกัน โดยความเข้าใจที่เกี่ยวกับโครงสร้างและคุณสมบัติทางชีวเคมีของ AbDHPAO สามารถนำไปสู่การใช้งานเอนไซม์นี้ในการใช้ประโยชน์ลิกนินจากชีวมวลได้ในอนาคต
Reference
Pimviriyakul P, Buttranon S, Soithongcharoen S, Suphawatkon C, Disayabootr K, Watthaisong P, Tinikul R, Jaruwat A, Chaiyen P, Chitnumsub P, Maenpuen S. Structure and biochemical characterization of an extradiol 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate 2,3-dioxygenase from Acinetobacter baumannii. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2023 Sep 26:109768.
DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2023.109768.
| Relevant SDGs | |
|---|---|
| BC investigator | |
 Asst. Prof. Ruchanok Tinikul Asst. Prof. Ruchanok Tinikul |
|