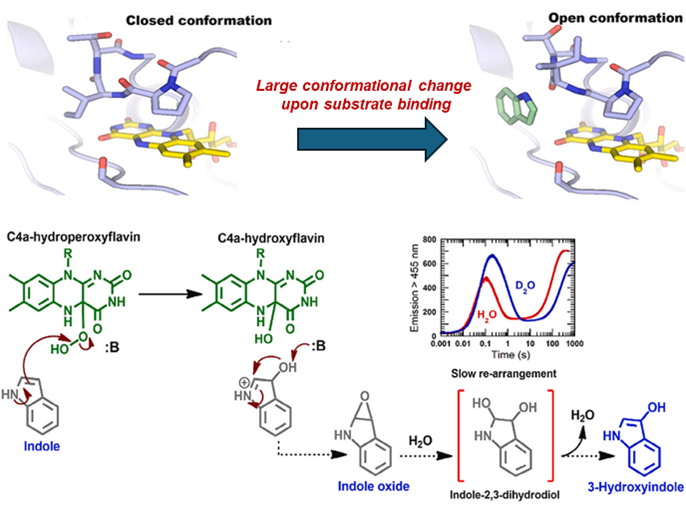
This study investigates how two-component indole monooxygenase from Acinetobacter baumannii converts indole into 3-hydroxyindole. The enzyme system consists of two cooperating proteins: reductase supplies reduced flavin, while the monooxygenase carries out the oxygenation reaction. We found that the reaction depends strongly on the presence of indole, which triggers structural changes in the oxygenase enzyme. Structural analysis revealed a flexible loop at the active site that can switch between closed and open forms, controlling whether the reactive oxygen intermediate can form. Kinetic experiments showed that indole binds preferentially to a specific enzyme–intermediate complex and that the overall reaction rate is limited by product or cofactor release. Our results indicate that the oxygenated indole product is released from the enzyme before it rearranges into 3-hydroxyindole outside the active site. These findings provide new insight into how two-component monooxygenase enzymes control reactivity and product formation.
โครงสร้างและกลไกปฏิกิริยาของเอนไซม์อินโดลโมโนออกซีจีเนสชนิดสององค์ประกอบจาก Acinetobacter baumannii
งานวิจัยนี้ศึกษากลไกของระบบเอนไซม์อินโดลโมโนออกซีจีเนส (two-component indole monooxygenase) จาก Acinetobacter baumannii ที่ทำหน้าที่เปลี่ยนอินโดลให้เป็น 3-ไฮดรอกซีอินโดล ระบบเอนไซม์ประกอบด้วยโปรตีนสองชนิดที่ทำงานร่วมกัน โดยรีดักเทส (reductase) ทำหน้าที่สร้างโคแฟกเตอร์ที่อยู่ในสภาพรีดิวซ์ ขณะที่โมโนออกซีจีเนส (monooxygenase) ทำหน้าที่เร่งปฏิกิริยาออกซิเดชัน จากการศึกษาพบว่า ประสิทธิภาพการเกิดปฏิกิริยาขึ้นอยู่กับการมีอยู่ของอินโดลสับสเตรท โดยอินโดลจะกระตุ้นให้เอนไซม์ออกซิเดสเกิดการเปลี่ยนแปลงโครงสร้าง การศึกษาทางโครงสร้างเผยให้เห็นบริเวณลูปที่มีความยืดหยุ่นในตำแหน่งออกฤทธิ์ของเอนไซม์ ซึ่งสามารถสลับระหว่างสภาพปิดและเปิดเพื่อควบคุมการเกิดตัวกลางปฏิกิริยาที่มีความไวต่อออกซิเจน การศึกษาด้านจลนศาสตร์แสดงให้เห็นว่าขั้นตอนการปล่อยผลิตภัณฑ์หรือโคแฟกเตอร์ออกจากเอนไซม์เป็นขั้นกำหนดอัตราปฏิกิริยา ผลลัพธ์บ่งชี้ว่าสารอินโดลที่ถูกออกซิไดซ์จะถูกปลดปล่อยออกจากเอนไซม์ก่อน แล้วจึงเกิดการปรับโครงสร้างต่อไปนอกตำแหน่งออกฤทธิ์จนกลายเป็น 3-ไฮดรอกซีอินโดล งานวิจัยนี้ช่วยเพิ่มความเข้าใจเกี่ยวกับการควบคุมปฏิกิริยาและการสร้างผลิตภัณฑ์ของเอนไซม์โมโนออกซีจีเนสชนิดสององค์ประกอบ
Reference
Suksomjaisaman K, Thananon K, Mangkalee M, Thotsaporn K, Tinikul R, Schulte A, Wangkanont K, Sirikantaramas S, Sucharitakul J, Chaiyen P. Structure and reaction mechanisms of a two-component indole monooxygenase from Acinetobacter baumannii. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2026, 776, 110681.
Relevant SDGs

BC investigator

