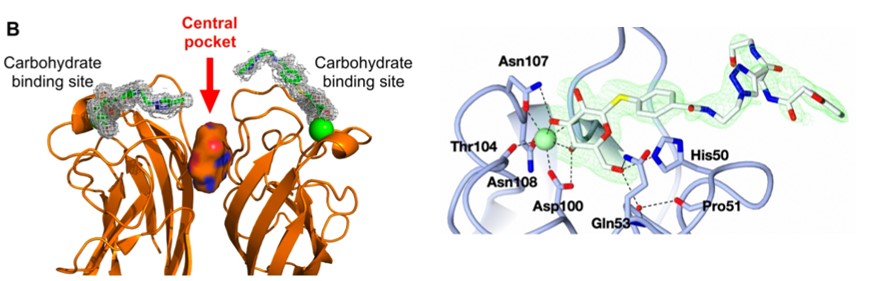
LecA is a carbohydrate-binding protein released by an opportunistic bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa, as part of a myriad of virulence factors and thus, a prime therapeutic target. In this work, we located a central pocket between two carbohydrate binding sites on LecA and designed a novel class of inhibitors that simultaneously target the central cavity and the two neighbouring carbohydrate binding sites. Biophysical assays such as SPR and ITC were used to confirm the inhibitor-LecA binding affinities in low-micromolar range. X-ray crystal structure of LecA in complex with the novel inhibitor revealed detailed interactions, which may aid the future design of novel LecA inhibitors.
(Source: https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.202100563)
References
Siebs E, Shanina E, Kuhaudomlarp S, da Silva Figueiredo Celestino Gomes P, Fortin C, Seeberger PH, Rognan D, Rademacher C, Imberty A, Titz A. Targeting the Central Pocket of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lectin LecA. Chembiochem. 2022 Feb 4;23(3):e202100563
| Relevant SDGs | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| BC investigator | |
 Dr. Sakonwan Kuhaudomlarp Dr. Sakonwan Kuhaudomlarp |
