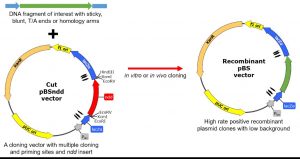
This is another approach to reduce background colonies, or false positive clones that may be arisen from intact or self-ligated plasmid in molecular cloning. Two plasmids, pBS2ndd and pBS3ndd, which resistant to ampicillin and kanamycin respectively. The plasmids carry ndd, a lethal gene from bacteriophage T4 coding for nucleoid disruption protein that binds to the host chromosome and progressively kill the cell. The deadly toxicity of Ndd inhibits host cells that obtain intact or ndd-religated vector from growing, which results in low background and dramatically reduces the effort for selection of recombinants. Moreover, the multiple cloning site was designed to support sticky-ends ligation with XcmI allows for in vitro T/A ligation, while with EcoRV permits blunt-end ligation, with capability of blue-white colony screening. In vivo homologous recombination cloning with universal priming sites of PCR insert fragments using primers containing universal homology arms and transformation into capable E. coli strains. The cloning for protein expression with blue-white selection was also possible using egfp as a model regulated by lac and T7 promoters on the plasmid or other build-in promoters with the insert.
Reference
Rotchanapreeda T, Ngonsawan W, Klomtun M, Jamorn Somana J. The plasmid vectors, pBS2ndd and pBS3ndd, for versatile cloning with low background in Escherichia coli. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 2018, 34(85) 1-27.
DOI: 10.1007/s11274-018-2466-z
| Relevant SDGs | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| BC investigator | |
 Asst. Prof. Jamorn Somana Asst. Prof. Jamorn Somana |
|
