A Minimized chemoenzymatic cascade for bacterial luciferase in bioreporter applications
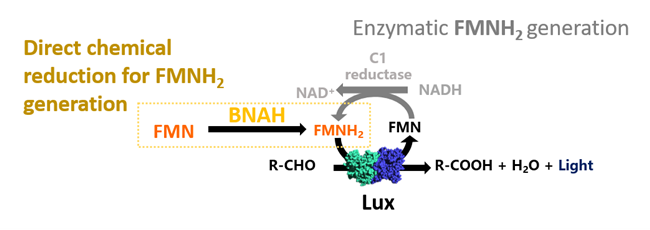
Bacterial luciferase (Lux) generates bioluminescent reaction by using long chain aldehyde, reduced FMN (FMNH2) and oxygen. As ability to generate light, Lux has widely been exploited as reporter system in many biotechnological and biomedical researches. However, the assay requires reaction of FMN reductase to generate FMNH2 using NADH substrate. This research has successfully developed a minimized auxiliary reaction to supply the FMNH2 using a nicotinamide biomimetic called 1-benzyl-1,4-dihydronicotinamide (BNAH). The BNAH is consider to be cheaper alternative chemical to NADH in the Lux assay to lower the assay cost. The reaction can proceed a direct reduction of FMN to FMNH2 without the requirement of the flavin reductase enzyme. The minimized cascade using BNAH can serve as a more simplified and cost-effective means for conducting Lux-based bioluminescence assays for further developed high-throughput platform.
Reference:
Phonbuppha J, Tinikul R, Wongnate T, Intasian P, Hollmann F, Paul CE, Chaiyen P. A Minimized Chemoenzymatic Cascade for Bacterial Luciferase in Bioreporter Applications. Chembiochem. 2020 Jul 16;21(14):2073-2079. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202000100.
| Relevant SDGs | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| BC investigator | |
 Asst. Prof. Ruchanok Tinikul Asst. Prof. Ruchanok Tinikul |
