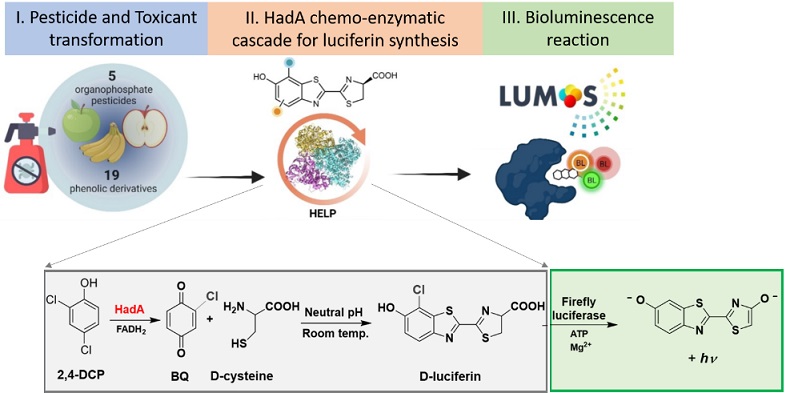
This research reported a novel, efficient, and green method to use enzymatic cascades, including esterase for pesticide transformation, flavin monooxygenase (HadA) for dehalogenation, flavin reductase and formate dehydrogenase for co-substrate regeneration, to synthesize high-value L-luciferin and its derivatives from organophosphate pesticides (called the HELP reaction). When this cascade is combined with a bioluminescence reaction catalyzed by firefly luciferase, we can convert the reaction into a new pesticide detection technology (called LUMOS technology) that provides a light signal in the presence of pesticides. By using a series of enzyme engineering and process optimization, the system can ultimately provide better detection sensitivity down to parts per trillion (ppt) levels that can overcome the classical chromatographic detection method. It not only provides a better sensitivity but can directly detect organophosphate pesticides in samples without requiring sample pretreatment. Therefore, these reported technologies will become a powerful tool for green synthesis of L-luciferin derivatives and for pesticide detection required in food and environmental quality controls.
Reference
Watthaisong P, Kamutira P, Kesornpun C, Pongsupasa V, Phonbuppha J, Tinikul R, Maenpuen S, Wongnate T, Nishihara R, Ohmiya Y, Chaiyen P. Luciferin synthesis and pesticide detection by luminescence enzymatic cascades. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202116908.
| Relevant SDGs | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| BC investigator | |
 Asst. Prof. Ruchanok Tinikul Asst. Prof. Ruchanok Tinikul |
