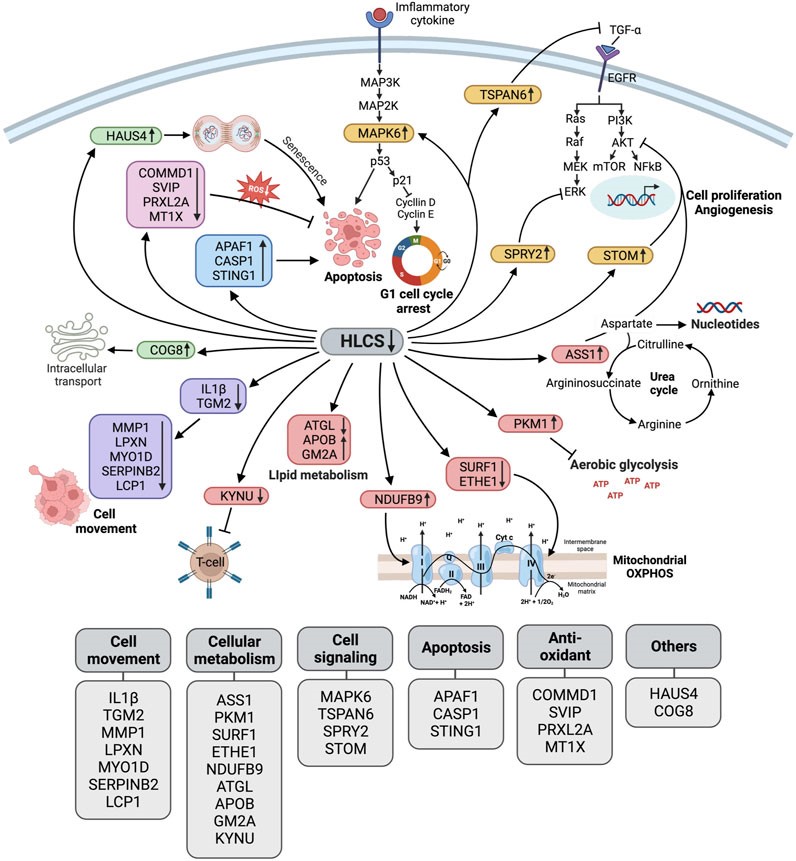
Holocarboxylase synthetase (HLCS) is the enzyme that regulates biotin carboxylase activities, and plays an important role in cancer metabolism. Here, we investigated the global biochemical changes associated with HLCS knockdown in MDA-MB-231 cells to discern the pathways that involve HLCS. Proteomic analysis of two independent HLCS knockdown cell lines identified 347 differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) whose expression change > 2-fold relative to the control cell line. Bioinformatic analysis showed that these proteins were mainly associated with the cellular process such as cell response to stimulus, cellular component organization or biogenesis, metabolism, biological regulation and signaling. Collectively, our study provides biochemical insights into how suppression of this gene perturbs growth and invasion of triple negative breast cancers, and suggests that HLCS can be an anti-cancer drug target.
เอ็นไซม์โฮโลคาร์บอกซิเลสซินธีเทส (HLCS) เป็นเอนไซม์ที่เร่งปฏิกิริยาการเติมหมู่ไบโอตินให้กลุ่มเอ็นไซม์ไบโอตินคาร์บอกซิเลส ซึ่งสำคัญต่อขบวนการเมตาบอลิซึมพื้นฐานในเซลล์ จากการศึกษาก่อนหน้านี้พบว่าการแสดงออกของเอ็นไซม์ HLCS มีระดับสูงขึ้นในเนื้อเยื่อมะเร็งของผู้ป่วยมะเร็งเต้านม และการยับยั้งการแสดงออกของเอ็นไซม์ HLCS ในเซลล์มะเร็งเต้านมเพาะเลี้ยง MDA-MB-231 สามารถลดอัตราการเจริญเติบโตและการเคลื่อนที่ของเซลล์มะเร็งได้ ผลการวิเคราะห์โปรทีโอมิกส์ในกลุ่มทดสอบเทียบกับกลุ่มควบคุม พบว่า HLCS knockdown cell lines มีโปรตีนที่มีการแสดงออกแตกต่างกันอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ รวม 347 ชนิด ซึ่งโปรตีนดังกล่าวเกี่ยวข้องกับขบวนการภายในเซลล์ ได้แก่ ขบวนการเมตาบอลิซึม การตอบสนองของเซลล์ต่อสิ่งเร้าการจัดระเบียบหรือการสังเคราะห์ส่วนประกอบของเซลล์ การควบคุมทางชีวภาพ และการส่งสัญญาณภายในเซลล์ จากผลการศึกษาครั้งนี้แสดงให้เห็นถึงบทบาทสำคัญของเอ็นไซม์ HLCS ต่อระบบเมตาบอลิซึมและขบวนการต่าง ๆ ภายในเซลล์ที่เกื้อหนุนการเจริญเติบโตและการเคลื่อนที่ของเซลล์มะเร็ง
Reference:
Sukjoi W, Young C, Acland M, Siritutsoontorn S, Roytrakul S, Klingler-Hoffmann M, Hoffmann P and Jitrapakdee S (2024) Proteomic analysis of holocarboxylase synthetase deficient-MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells revealed the biochemical changes associated with cell death, impaired growth signaling, and metabolism. Front. Mol. Biosci. 10:1250423.
DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1250423
Relevant SDGs

BC investigator

