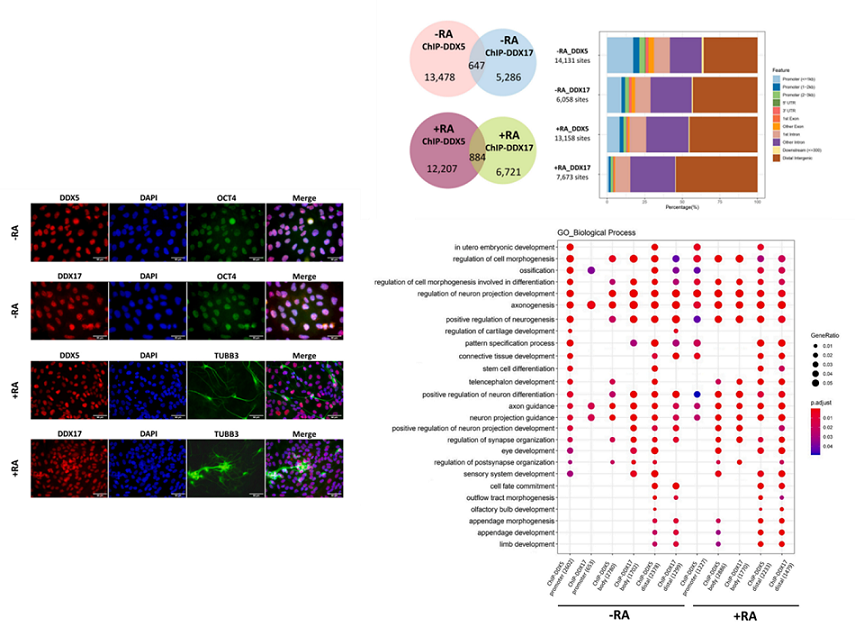
Understanding human neurogenesis is critical toward regenerative medicine for neurodegeneration. However, little is known how neural differentiation is regulated by DEAD box-containing RNA helicases, which comprise a diverse class of RNA remodeling enzymes. We show here that expression of DDX5 and DDX17 is abundant throughout neural differentiation of NTERA2, and is mostly localized within the nucleus. The two RNA helicases occupy chromatin genome-wide at regions associated with neurogenesis-related genes in both hPSCs and their neural derivatives. Further, both DDX5 and DDX17 are mutually required for controlling transcriptional expression of these genes, but are not important for maintenance of stem cell state of hPSCs. In contrast, they facilitate early neural differentiation of hPSCs, generation of neurospheres from the stem cells, and transcriptional expression of key neurogenic transcription factors such as SOX1 and PAX6 during neural differentiation. Importantly, DDX5 and DDX17 are critical for differentiation of hPSCs toward NESTIN- and TUBB3-positive cells, which represent neural progenitors and mature neurons, respectively.
Reference:
Suthapot P, Xiao T, Felsenfeld G, Hongeng S, Wongtrakoongate P. The RNA helicases DDX5 and DDX17 facilitate neural differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells NTERA2. Life Sci. 2022 Feb 15;291:120298. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120298.
| Relevant SDGs | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| BC investigator | |
 Assoc. Prof. Patompon Wongtrakoongate Assoc. Prof. Patompon Wongtrakoongate |