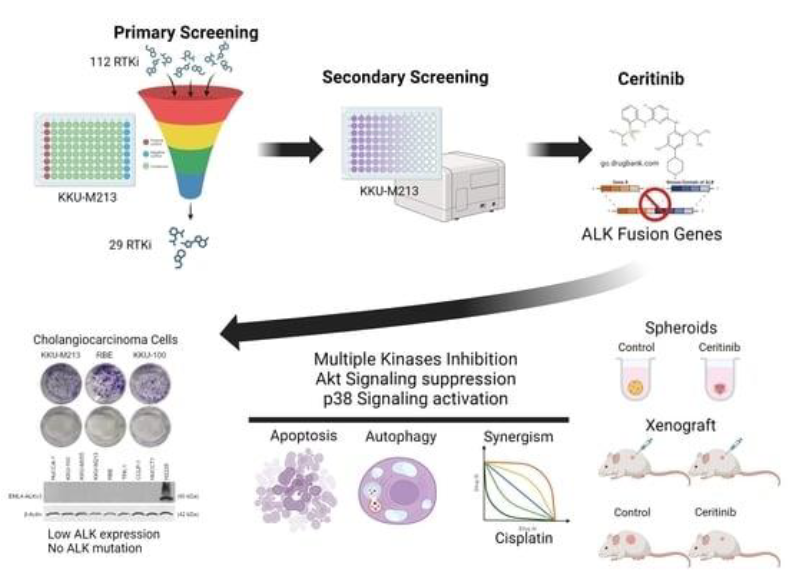
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a difficult-to-treat cancer, with limited therapeutic options and surgery being the only curative treatment. Standard chemotherapy involves gemcitabine-based therapies combined with cisplatin, oxaliplatin, capecitabine, or 5-FU with a dismal prognosis for most patients. Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are aberrantly expressed in CCAs encompassing potential therapeutic opportunity. Hence, 112 RTK inhibitors were screened in KKU-M213 cells, and ceritinib, an approved targeted therapy for ALK-fusion gene driven cancers, was the most potent candidate. Ceritinib’s cytotoxicity in CCA was assessed using MTT and clonogenic assays, along with immunofluorescence, western blot, and qRT-PCR techniques to analyze gene expression and signaling changes. Furthermore, the drug interaction relationship between ceritinib and cisplatin was determined using a ZIP synergy score. Additionally, spheroid and xenograft models were employed to investigate the efficacy of ceritinib in vivo. Our study revealed that ceritinib effectively killed CCA cells at clinically relevant plasma concentrations, irrespective of ALK expression or mutation status. Ceritinib modulated multiple signaling pathways leading to the inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and activated both apoptosis and autophagy. Additionally, ceritinib and cisplatin synergistically reduced CCA cell viability. Our data show ceritinib as an effective treatment of CCA, which could be potentially explored in the other cancer types without ALK mutations.
มะเร็งท่อน้ำดี เป็นมะเร็งที่มีความรุนแรงมาก ขณะนี้การรักษาส่วนใหญ่ยังใช้ยาเคมีบำบัด (standard chemotherapy) แต่ก็มักจะไม่ได้ผล ดังนั้นจึงมีความจำเป็นที่จะต้องหายาใหม่ที่มีประสิทธิภาพสำหรับผู้ป่วยมะเร็งท่อน้ำดี ในงานนี้เราคัดกรองยาประเภทมุ่งเป้า (targeted therapy) 112 ชนิดโดยใช้เซลล์ไลน์ KKU-M213 และพบว่า Ceritinib มีฤทธิ์ยับยั้งเซลล์มะเร็งท่อน้ำดีได้ดีที่สุด ปกติแล้ว Ceritinib ได้รับการรับรองให้ใช้รักษาผู้ป่วยมะเร็งปอดชนิด non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) ที่มีการผ่าเหล่าของ ALK gene (ALK-positive NSCLC) ซึ่งยังจำกัดการใช้อยู่ในวงแคบเฉพาะผู้ป่วยที่มี ALK mutation เท่านั้น อย่างไรก็ตาม ยังไม่มีการรับรองให้ใช้ Ceritinib ในการรักษามะเร็งท่อน้ำดีเนื่องจากมะเร็งท่อน้ำดีส่วนใหญ่ไม่แสดงออก/แสดงออก ALK ในระดับที่ต่ำมาก งานวิจัยนี้แสดงให้เห็นเป็นครั้งแรกว่า Ceritinib มีศักยภาพในการยับยั้งเซลล์มะเร็งท่อน้ำดีทั้งในระดับเซลล์ไลน์ในห้องปฏิบัติการ (in vitro) และ ในหนูทดลอง (in vivo) ข้อสำคัญ การทดลองของเราแสดงว่า Ceritinib ออกฤทธิ์ที่ระดับความเข้มข้นที่เหมาะสม และ เซลล์มะเร็งท่อน้ำดีที่เป็นเป้าหมายไม่จำเป็นต้องมี ALK mutation ซึ่งแสดงให้เห็นถึงศักยภาพของ Ceritinib ที่จะใช้รักษาผู้ป่วยมะเร็งในวงกว้างและไม่จำกัดเพียงเฉพาะกลุ่มที่มี ALK mutation เท่านั้น ซึ่งงานนี้อาจขยายผลทดสอบในมะเร็งชนิดอื่นๆที่ไม่มี ALK mutation เพื่อที่จะใช้ Ceritinib ให้เป็นประโยชน์ต่อผู้ป่วยในวงกว้างมากขึ้นต่อไป
Reference
Myint KZ, Balasubramanian B, Venkatraman S, Phimsen S, Sripramote S, Jantra J, Choeiphuk C, Mingphruedhi S, Muangkaew P, Rungsakulkij N, Tangtawee P, Suragul W, Farquharson WV, Wongprasert K, Chutipongtanate S, Sanvarinda P, Ponpuak M, Poungvarin N, Janvilisri T, Suthiphongchai T, Yacqub-Usman K, Grabowska AM, Bates DO, Tohtong R. Therapeutic Implications of Ceritinib in Cholangiocarcinoma beyond ALK Expression and Mutation. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Feb 2;17(2):197.
DOI: 10.3390/ph17020197.
| Relevant SDGs | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| BC investigator | |
 Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong |
|
